Purpose
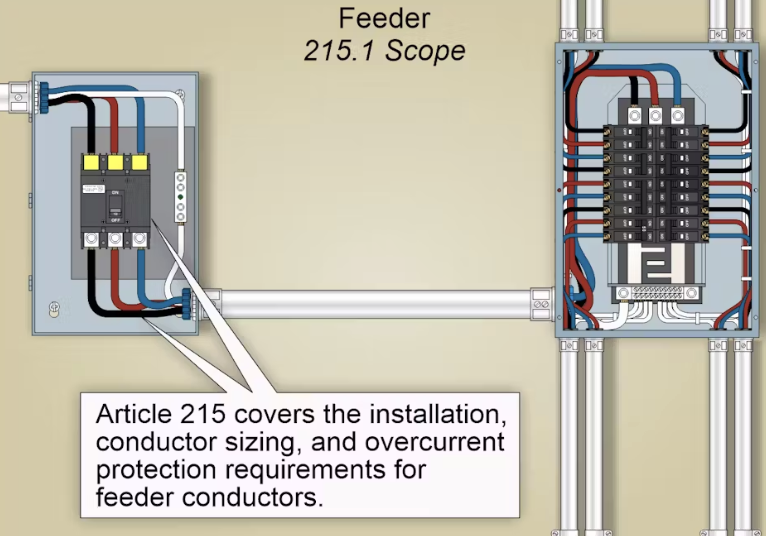
Article 215 of the National Electrical Code® (NEC®) establishes the requirements for the installation, sizing, and protection of feeder circuits — the conductors that carry power from the service equipment to branch circuit panels or distribution equipment.
Proper feeder design ensures safe power delivery without overheating or voltage drop.
Key Concepts
- Definition (215.2) A feeder is all circuit conductors between the service equipment (or separately derived system) and the final branch circuit overcurrent device.
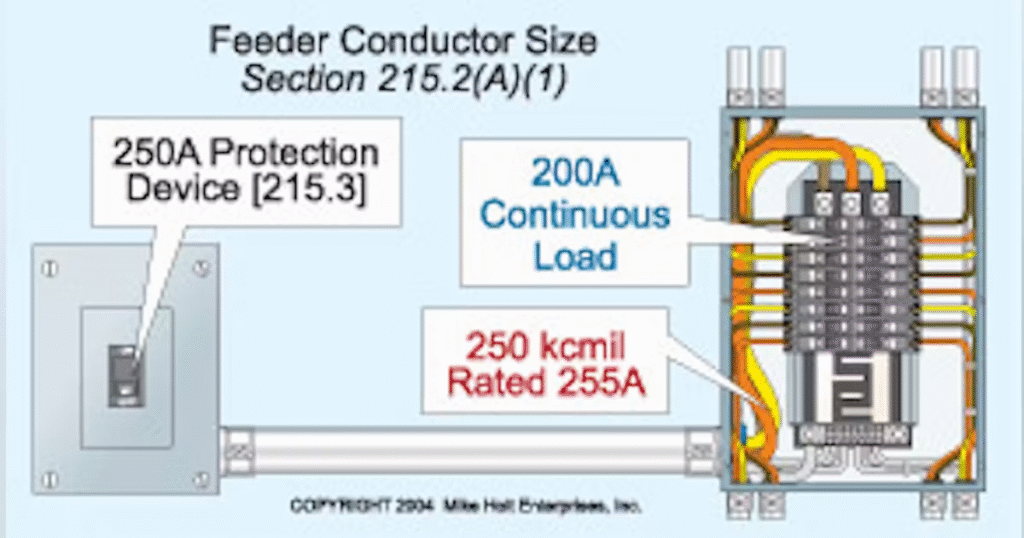
- Conductor Sizing (215.2(A))
- Feeders must have sufficient ampacity to handle the load served.
- Continuous loads must not exceed 80% of the feeder rating (sized at 125% of the continuous load).
- Apply voltage drop limits — feeders should not exceed 3% drop to maintain efficiency.
- Overcurrent Protection (215.3)
- Feeders require overcurrent devices rated to protect conductors per their ampacity (Article 240).
- Breakers or fuses must be located at the point where the feeder originates.
- Grounding & Bonding (215.6)
- Feeder equipment grounding conductors (EGCs) must be sized per Table 250.122.
- Grounded conductor (neutral) and EGC must be isolated in subpanels.
- Identification (215.12)
- Feeder conductors must be color-coded or labeled to distinguish ungrounded, grounded, and grounding conductors.
- Example:
- Black, red, blue — phase conductors
- White or gray — neutral
- Green or bare — equipment ground
- Multiple Feeders & Disconnects (215.5)
- Each feeder must have a main disconnecting means.
- If multiple feeders supply one area, they must be clearly marked to show their source.
- Ground-Fault Protection (215.10)
- Feeders supplying 800 A or more to 3-phase, 4-wire systems must include ground-fault protection.
- This protects large equipment and minimizes service interruptions.
⚙️ Key Takeaways
- Feeders carry large electrical loads — correct sizing and protection are critical.
- Always follow ampacity tables (310.16) and protection rules (240).
- Maintain clear identification, grounding, and disconnect labeling.
- Voltage drop and overcurrent protection are essential for system performance and safety.


