A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. It operates in reverse bias and generates current when exposed to light.
Working Principle
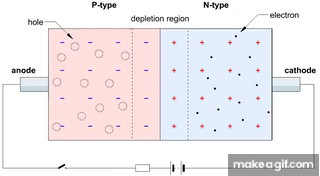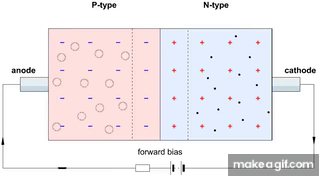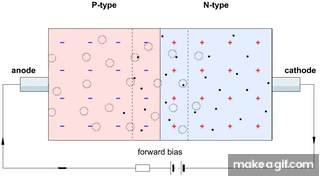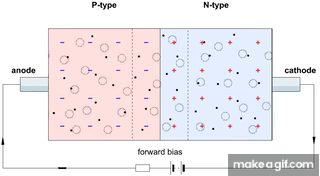
- A photodiode is made of a P-N junction.
- In reverse bias, the depletion region is wide, and very little current flows in darkness.
- When light photons hit the junction, they create electron-hole pairs.
- These carriers move across the junction, generating a photocurrent proportional to the light intensity.
Explanation of GIFs
- First GIF: Shows the P-N junction in reverse bias. When light falls on the junction, electrons and holes are generated and flow, producing current.
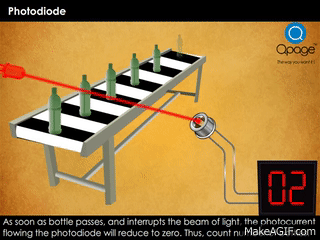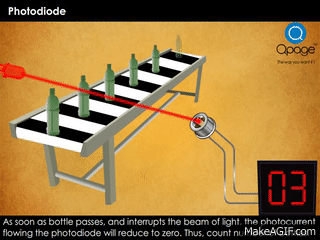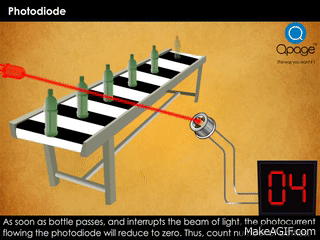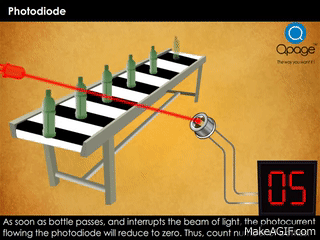
- Second GIF: Shows a practical use case. A light beam falls on the photodiode. When a bottle interrupts the beam, the current drops, allowing the system to count the object.
Applications
- Light detection and measurement
- Optical communication systems
- Safety and security sensors
- Object counters in factories
- Solar cells (special type of photodiode)
✅ Key Point: A photodiode is like the eye of electronics—it senses light and turns it into electrical signals for use in different applications.


