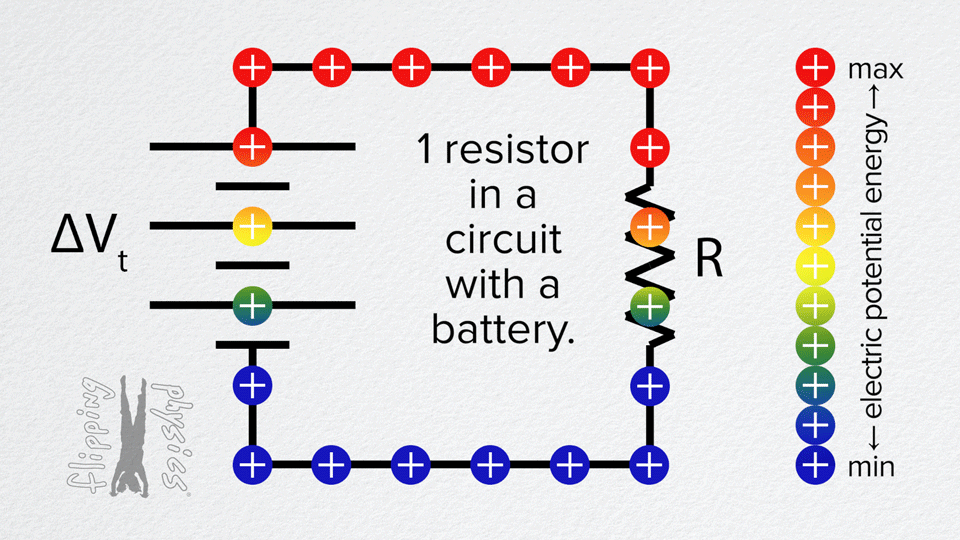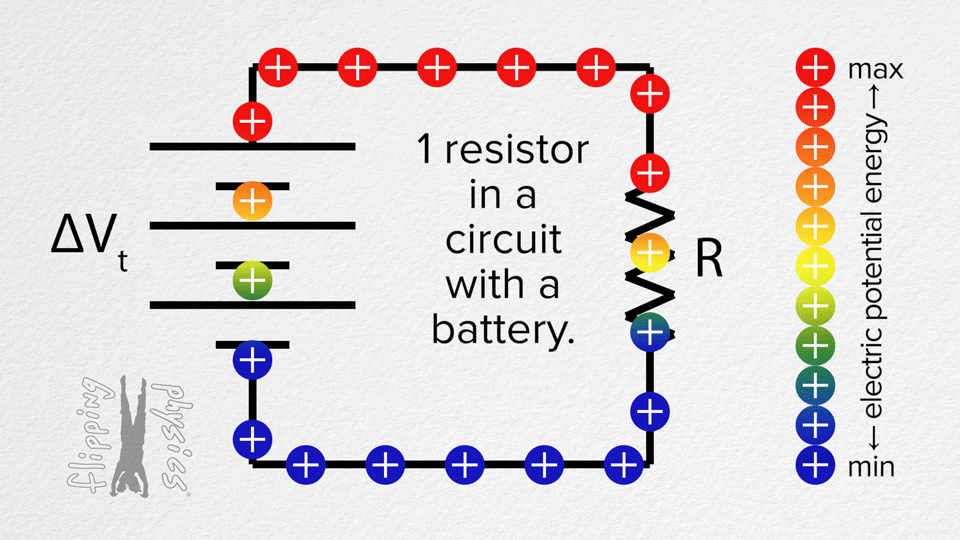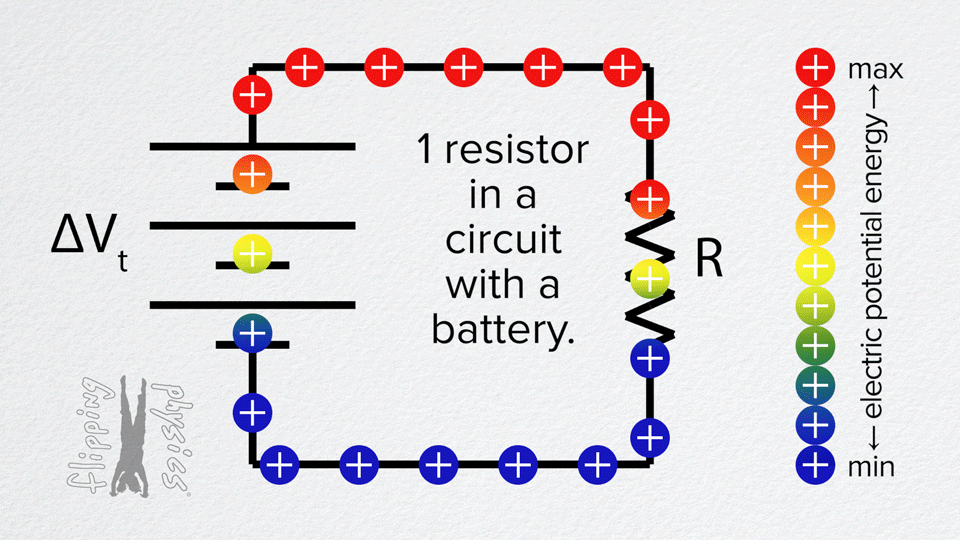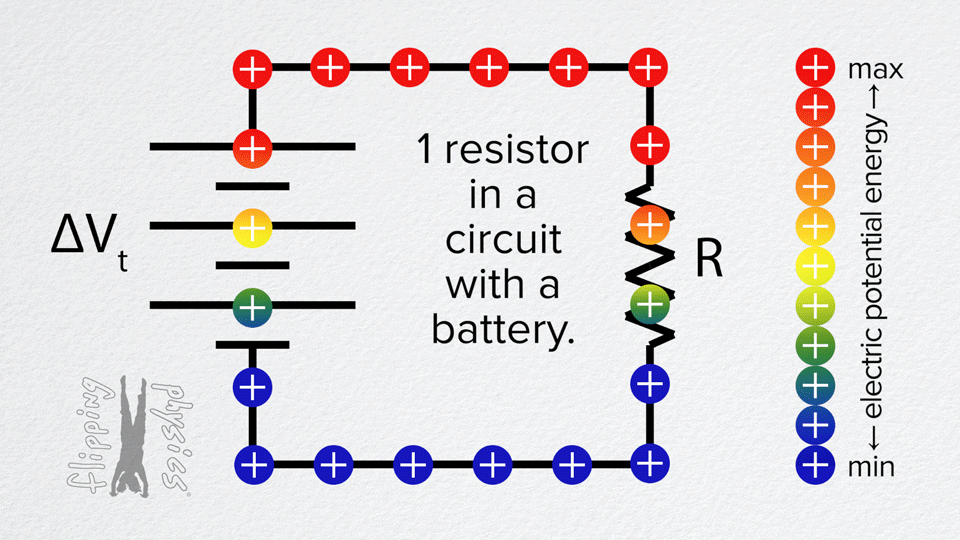
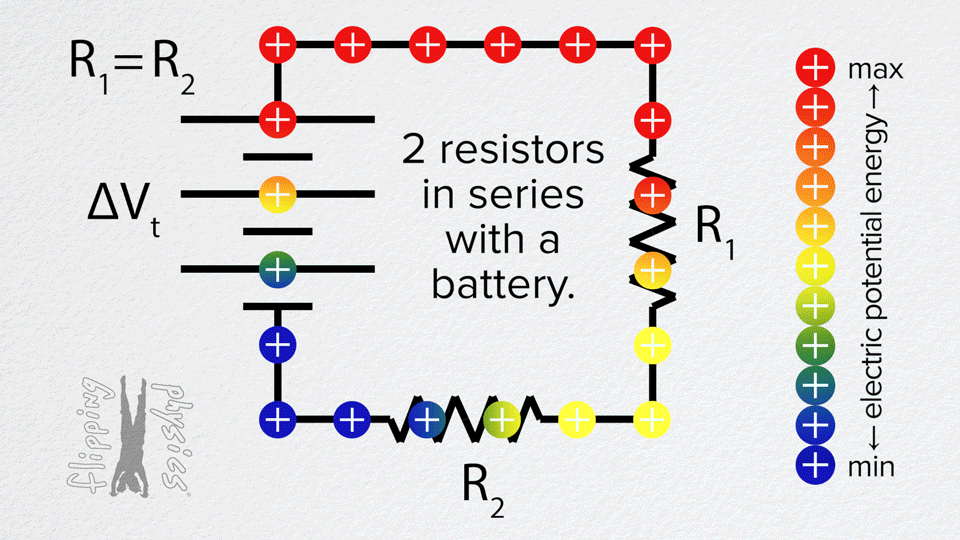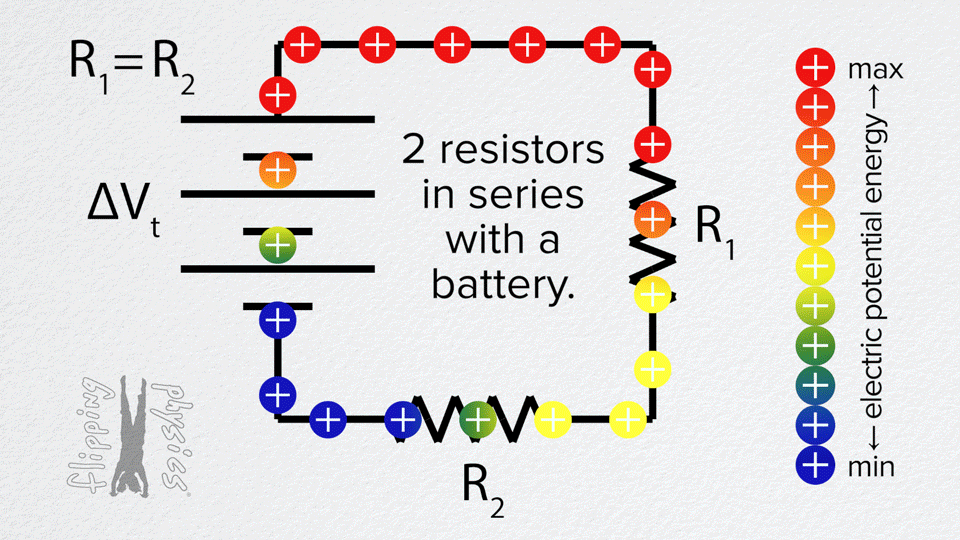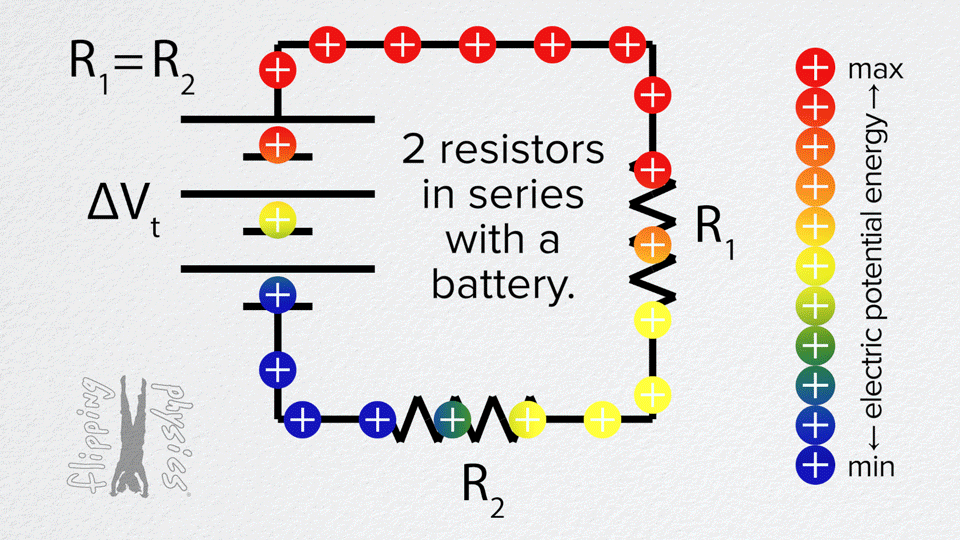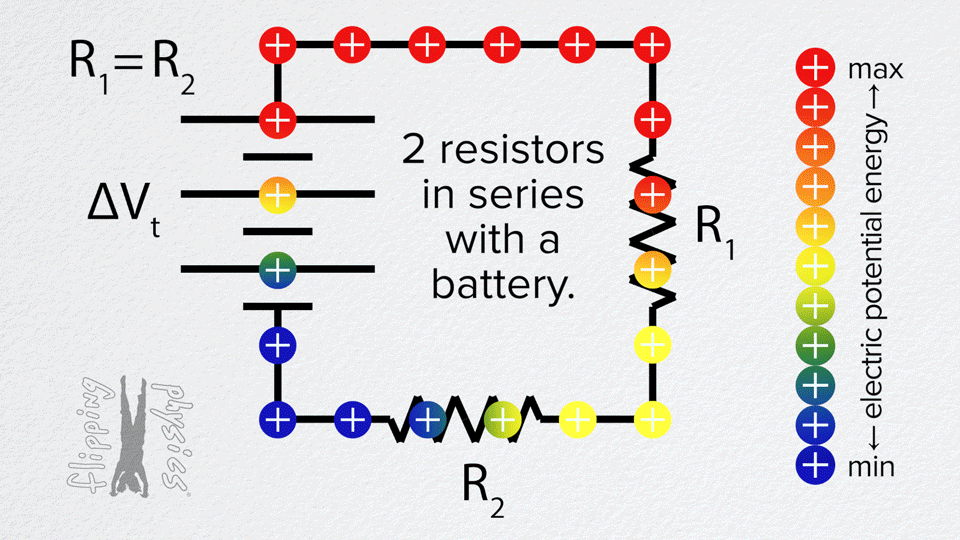
Resistors in Series
- The same current flows through each resistor one after another.
- Total resistance is the sum: R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 + …
- The voltage from the battery is divided across the resistors.
Example: Two 10 Ω resistors in series → R_total = 20 Ω
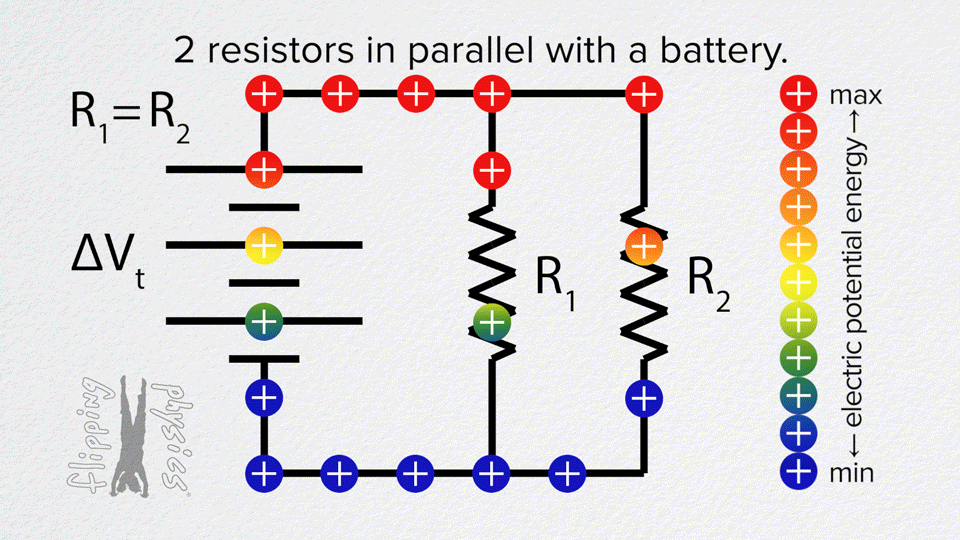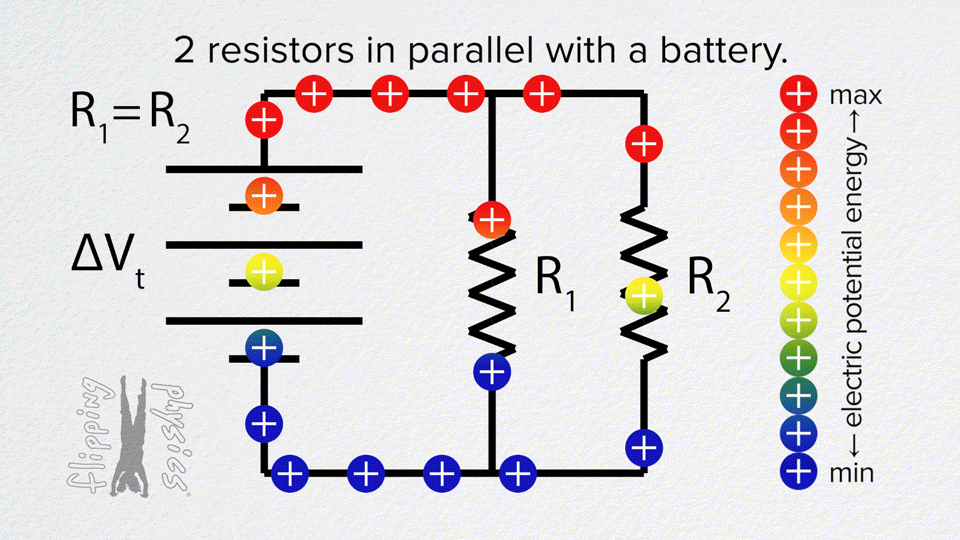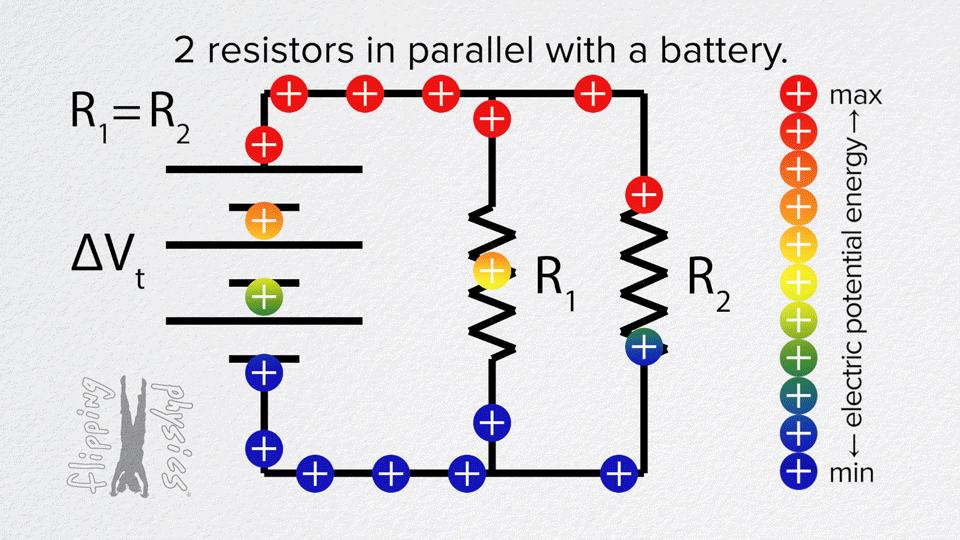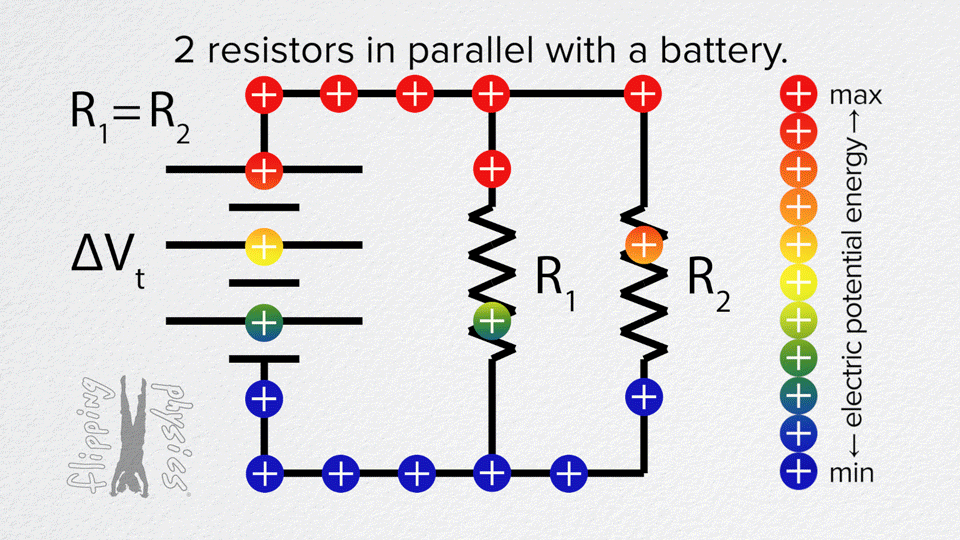
Resistors in Parallel
- Each resistor is connected across the same two points.
- Voltage is the same across all resistors.
- Total resistance is always smaller than the smallest resistor: 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + …
- Current splits between the different paths.
Example: Two 10 Ω resistors in parallel → R_total = 5 Ω


