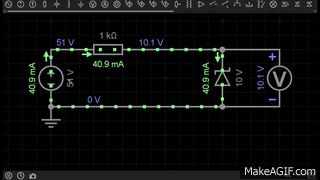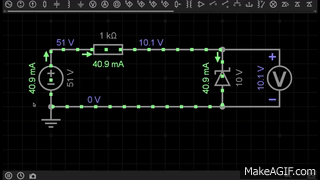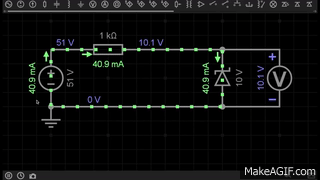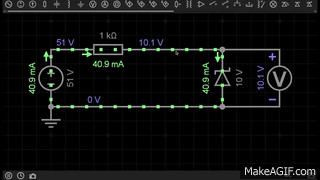
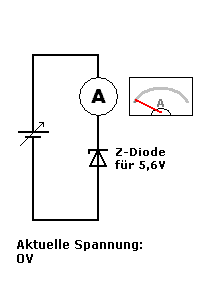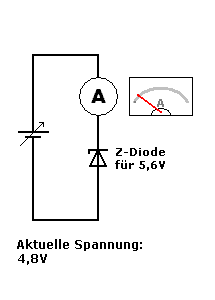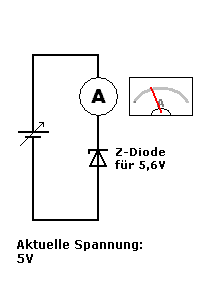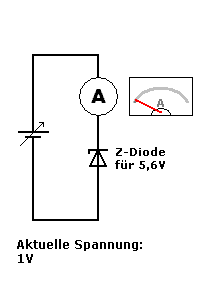
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to allow current to flow not only in the forward direction (like a normal diode) but also in the reverse direction when the voltage reaches a specific value called the Zener breakdown voltage.
Working Principle (GIF Reference)
- In the GIF, the Zener diode is placed in reverse bias.
- When the applied voltage is below the breakdown voltage (e.g., 5.6V), almost no current flows through the diode.
- Once the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage (Vz), the diode starts conducting in reverse, maintaining a stable output voltage across the load.
- This makes the Zener diode very useful for voltage regulation in circuits.
Key Features
- Zener Breakdown Voltage (Vz): Fixed value (e.g., 5.1V, 5.6V, 10V, etc.), at which the diode conducts in reverse.
- Reverse Bias Operation: Unlike normal diodes, Zener diodes are specifically designed to work in reverse bias mode.
- Voltage Regulation: Keeps the output voltage nearly constant even if the input voltage changes.
Applications
- Voltage Regulator – Provides a stable reference voltage.
- Overvoltage Protection – Protects sensitive circuits from high voltage surges.
- Waveform Clipping & Shaping – Used in signal conditioning.
👉 In the first GIF, the Zener diode clamps the voltage at 10V, showing its regulation property.
👉 In the second GIF, as the supply voltage increases, the Zener begins to conduct at 5.6V, keeping the voltage across it stable.


