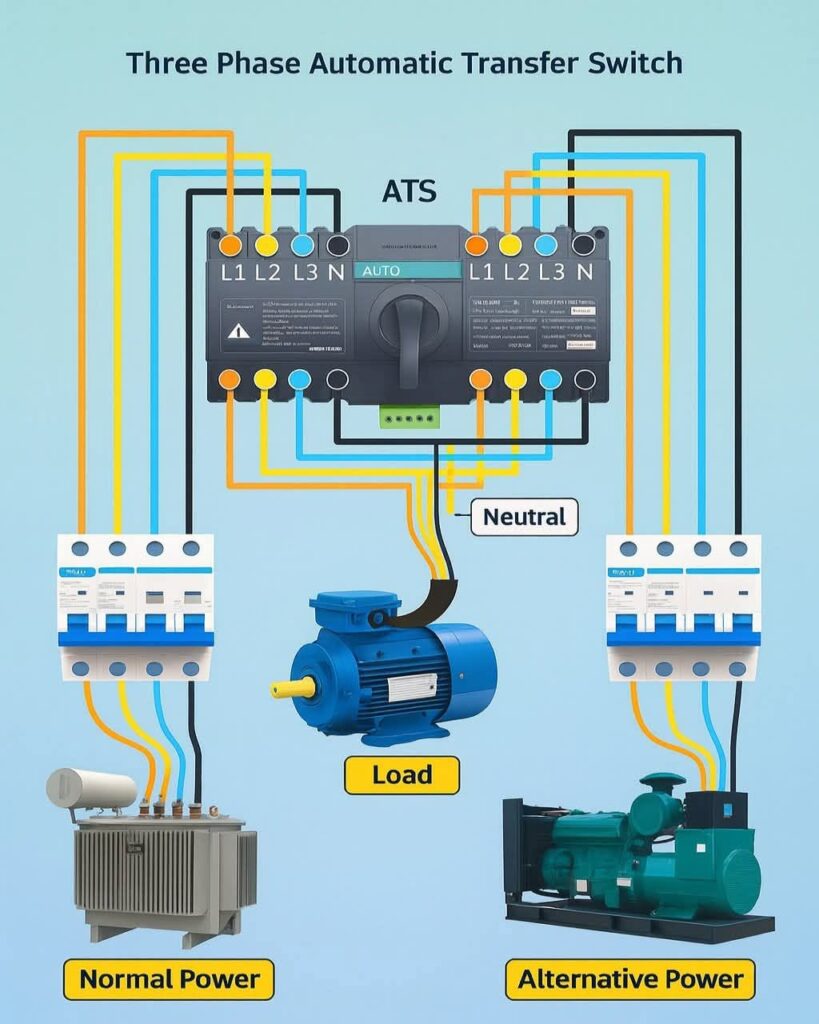
This diagram shows a Three Phase Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) system — a smart electrical setup that automatically switches the power supply between normal power (utility) and alternative power (generator) in case of power failure.
It ensures uninterrupted power supply to essential loads, making it ideal for industries, hospitals, offices, and data centers where continuous operation is critical.
Key Components:
- ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch): The central unit that automatically transfers the electrical load between the normal and alternative power sources depending on availability.
- Normal Power Source: Usually the main utility power or transformer supply that powers the system under normal conditions.
- Alternative Power Source: Typically a generator set (genset) that provides backup power during a mains outage.
- MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers): Installed on both power inputs to protect the system from overloads or short circuits.
- Neutral Line: Provides a common return path for the current from both power sources.
- Load (Motor or Equipment): The connected device or system that receives continuous power through the ATS.
Working Principle:
Under normal conditions, the ATS connects the load to the main (normal) power source.
When the utility power fails, the ATS automatically detects the outage and switches the load to the alternative (generator) power source.
Once the main supply is restored, the ATS transfers the load back to normal power and disconnects the generator.
This automatic switching mechanism ensures a smooth and quick transition without manual intervention, preventing downtime or equipment damage.
⚡ Tip:
Ensure proper earthing and phase sequencing when installing the ATS system. Regularly test the transfer function to confirm reliable operation during emergencies.


