This animation explains how a transformer changes the voltage level of alternating current (AC).
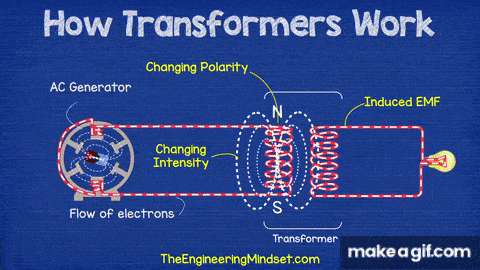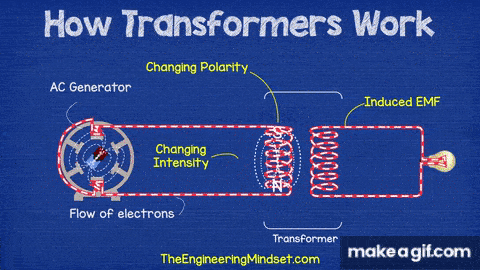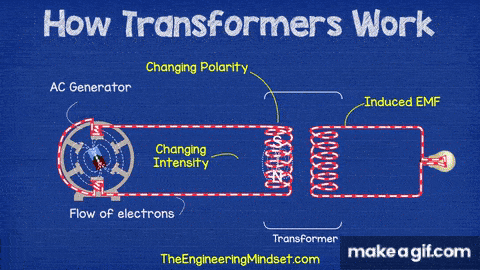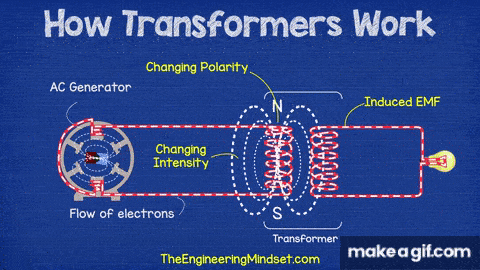
Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, transferring electrical energy from one coil to another without any direct electrical connection.
They are essential in power systems for stepping voltage up for transmission and down for safe distribution.
Key Components:
- AC Generator: Supplies the alternating current that changes polarity and intensity.
- Primary Coil (Input Coil): Connected to the AC source; creates a changing magnetic field.
- Core: A magnetic material that carries the changing magnetic field from the primary to the secondary coil.
- Secondary Coil (Output Coil): Receives the changing magnetic field and produces an induced voltage (EMF).
- Induced EMF: The voltage generated in the secondary coil due to magnetic induction.
Working Principle:
- The AC generator sends alternating current to the primary coil.
- As the current constantly changes direction and strength, it creates a changing magnetic field.
- This magnetic field flows through the core and reaches the secondary coil.
- The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil — this is called electromagnetic induction.
- Depending on the number of turns in each coil:
- More turns on the secondary = Step-up transformer
- Fewer turns on the secondary = Step-down transformer
Transformers allow efficient power transfer across long distances with minimal losses.
⚡ Tip:
Transformers only work with AC. They cannot operate with DC because DC does not produce a changing magnetic field.


