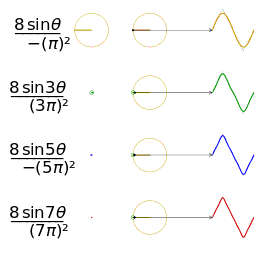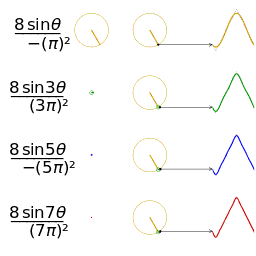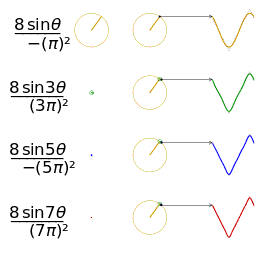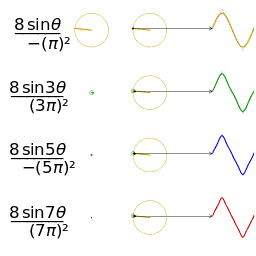
What a triangle wave is
- A triangle wave is a periodic waveform that linearly ramps up then linearly ramps down (or vice versa), forming a triangular shape.
- It has slope changes at the peaks (sharp corners), unlike sine waves which are smooth.
What Fourier series does here
- Fourier series lets you express a periodic waveform (like the triangle wave) as a sum of sines (or cosines) of different frequencies (harmonics), amplitudes, and phases.
- The animation shows how each harmonic “circle” contributes: each circle corresponds to one sine wave component. The bigger the circle (or the higher the amplitude), the more that harmonic contributes.
- When you sum enough of them, they build up to approximate the non-sinusoidal triangle shape.
- It’s a visualization of the Fourier series for a triangle wave.
- On one side (often using rotating circles / “harmonic circles”), you see multiple circular motions (each corresponding to one harmonic component).
- On the other side, those harmonic contributions add up over time to approximate the triangle wave. With more harmonics included, the sum more closely resembles a perfect triangle shape.


