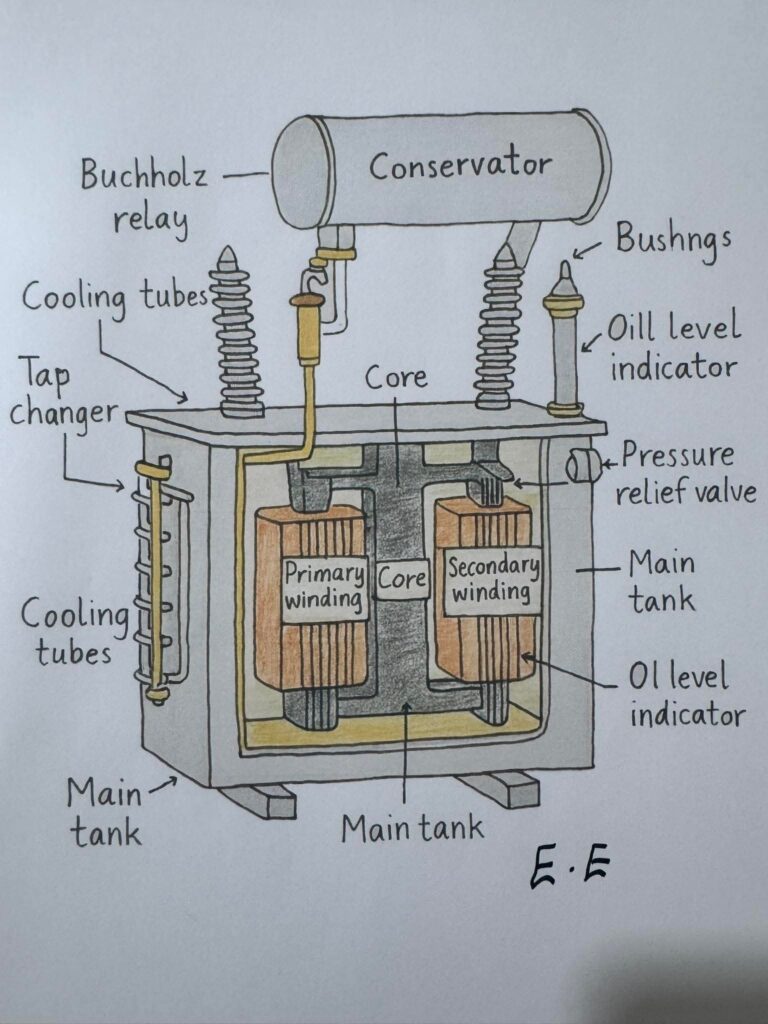
This diagram shows the internal and external parts of an oil-filled power transformer, an essential device used to step up or step down voltage in electrical systems.
The primary winding and secondary winding are wound on the core, which provides a magnetic path for energy transfer.The main tank holds the insulating oil that cools and insulates the transformer components, while cooling tubes help dissipate heat.
The conservator stores extra oil to maintain proper levels as temperature changes, and the Buchholz relay detects faults within the transformer.Other important parts include bushings for external electrical connections, a pressure relief valve for safety, and oil level indicators to monitor the oil condition.
Together, these components ensure efficient operation, insulation, and protection of the transformer in power systems.


