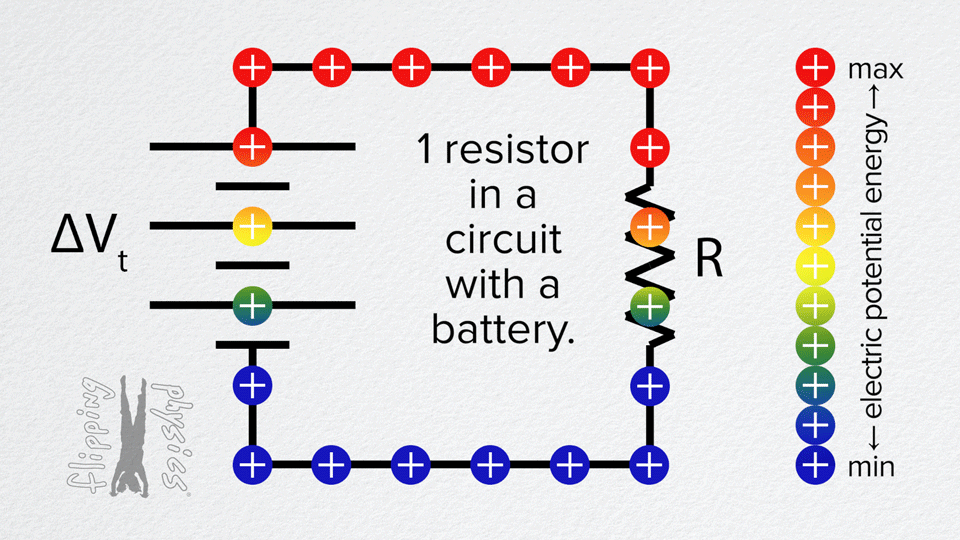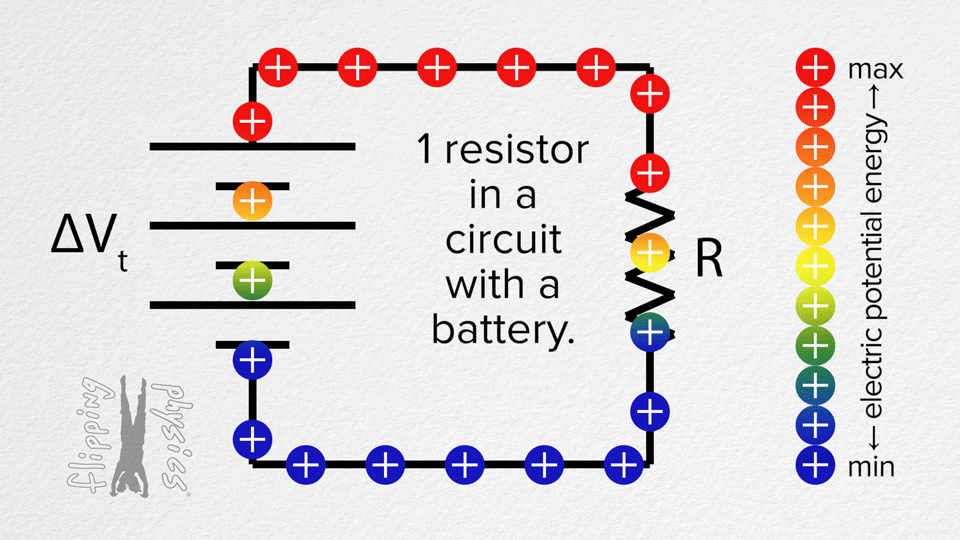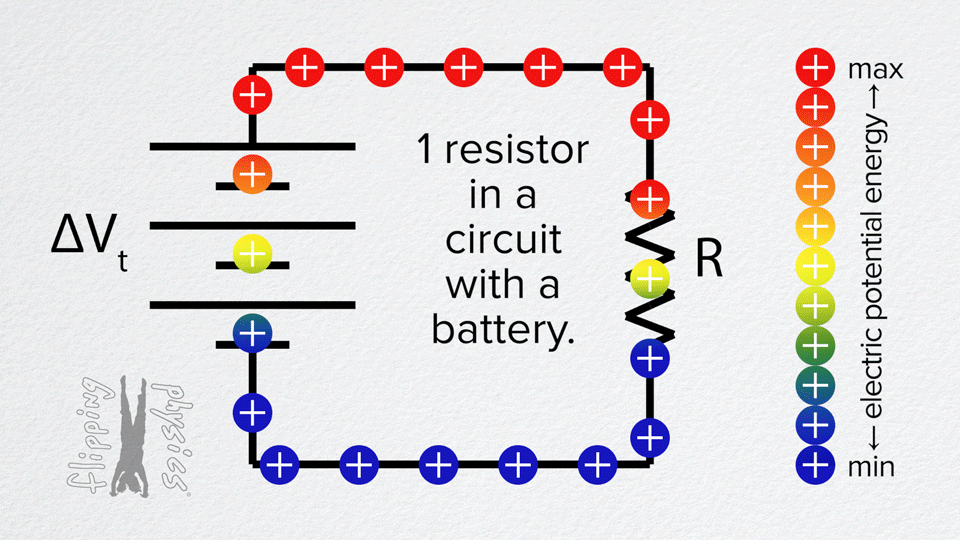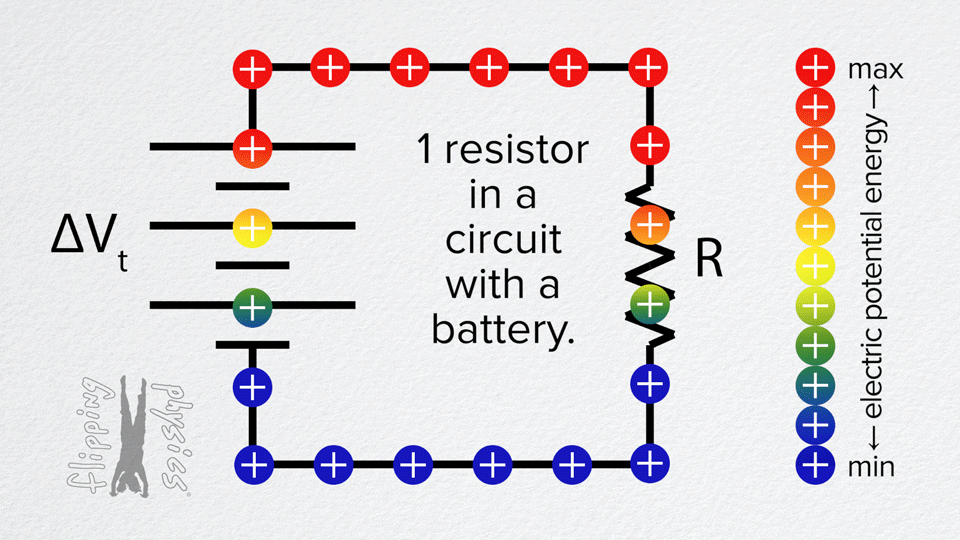
- A simple circuit with a single resistor connected to a voltage source (battery).
- Charges move through the resistor from the positive terminal of the source to the negative.
- The animation often shows little dots or markers representing electric charge or current flow.
From the resistor’s point of view
- The resistor resists the flow of electric current. That means it opposes the motion of charges, converting electrical energy into heat (or some form of energy loss inside the resistor).
- The rate of current (how many charges per second) depends on the voltage across the resistor and its resistance (Ohm’s Law: V = I · R).
Key effects you can
- When the circuit is closed, there is a steady current through the resistor. The charges move through it.
- The resistor drops voltage: there is a voltage difference across it (greater at the end closer to the positive terminal, lower closer to the negative).
- As current flows, power is dissipated: P = I²R or P = V² / R.


