NEC Table 250.66 is the standard for determining the size of the Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC) for alternating-current systems.
Grounding Electrode Conductor for Alternating-Current Systems
Use this table to determine the required size of the grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the largest ungrounded conductor in the raceway or cable.
| Size of Largest Ungrounded Conductor (AWG/kcmil) | Size of Grounding Electrode Conductor (AWG/kcmil) | ||
| Copper | Aluminum | Copper | Aluminum |
| 2 or smaller | 1/0 or smaller | 8 | 6 |
| 1 or 1/0 | 2/0 or 3/0 | 6 | 4 |
| 2/0 or 3/0 | 4/0 or 250 | 4 | 2 |
| Over 3/0 thru 350 | Over 250 thru 500 | 2 | 1/0 |
| Over 350 thru 600 | Over 500 thru 900 | 1/0 | 3/0 |
| Over 600 thru 1100 | Over 900 thru 1750 | 2/0 | 4/0 |
| Over 1100 | Over 1750 | 3/0 | 250 |
Note: Where multiple sets of service-entrance conductors are used (parallel sets), the “Size of Largest Ungrounded Conductor” is determined by the equivalent area of the parallel conductors added together.
The GEC connects the system grounded conductor or equipment to the grounding electrode system (e.g., ground rod, concrete-encased electrode, or building steel).
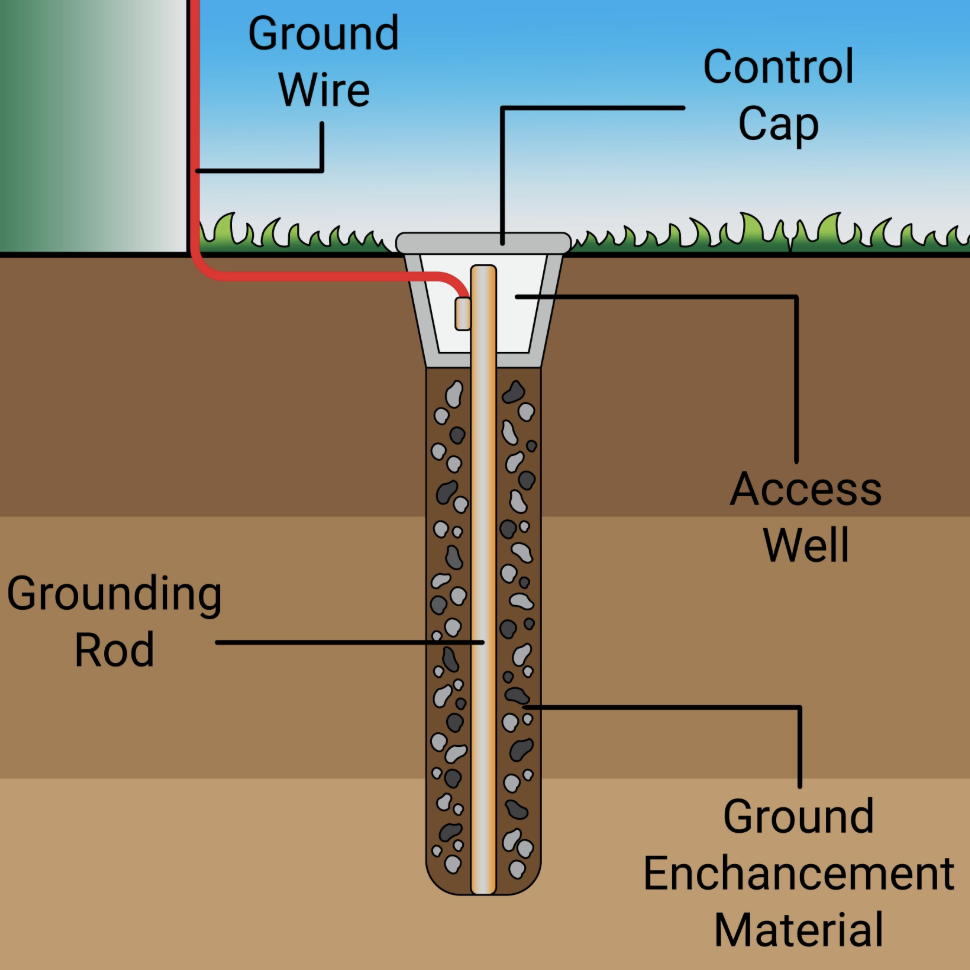
Purpose of the GEC: Unlike normal conductors, the GEC is not intended to carry current under normal conditions. Instead, it provides a safe path to the earth to limit voltage caused by:
- Lightning strikes
- Power line surges
- Unintentional contact with high-voltage lines
2020 Code Change: “Service-Entrance” Removed
What Changed: In previous editions, the table title referred to “Service-Entrance Conductors.” In the 2020 NEC®, the term “service-entrance” was deleted.
Why? This table is not limited to services. It is also used to size GECs for:
- Buildings supplied by feeders or branch circuits.
- Separately derived systems (transformers/generators).
How to Size the Conductor
The size of the Grounding Electrode Conductor is determined by the size of the largest ungrounded conductor (the hot wires) in the system.
Key Rule (Note 2): If the service-entrance conductors are not yet installed (e.g., the utility has not run the line yet), you must determine the GEC size based on the equivalent size of the largest conductor required for the load.
Exceptions & Special Rules
Not all electrodes require the full size listed in Table 250.66.
1. Sole Connections (Smaller Sizes Permitted) If the GEC connects only to specific electrodes, it does not need to be larger than specific sizes (per Section 250.66(A) through (C)):
- Ground Rods/Pipes: Maximum required size is usually limited (often 6 AWG Cu).
- Concrete-Encased Electrodes (Ufer): Maximum required size is usually limited (often 4 AWG Cu).
- Ground Rings: Size is limited to the size of the ring conductor.
2. Strict Adherence (Must Use Table) You must use the full values in Table 250.66 for:
- Underground metal water pipes.
- Metal in-ground support structures.


