What is an Inverter?
The inverter is an electronic device used to convert Direct Current(DC) into Alternating current(AC). The Alternating Current is a current that consistently changes its magnitude with respect to time. This current flows only in one direction. The Direct Current is also a one-directional current that usually flows through a conductor, but sometimes it can also flow through the insulators.
These inverters are used to the work that is opposite to the converters. It does not produce power, but the DC source also produces it. Usually, the inverter is an electronic device, but sometimes it can be made with mechanical components. They are ordinarily used in applications where voltages and high-current are present. The efficiency of the power inverter is more than 95%. The power inverters are also used in controlling speed and torque in electronic motors.

How does an inverter work?
An inverter supplies 220V or 110V AC to connected devices. When the main AC supply is available, the inverter detects it and routes the AC through a relay to both the load and the battery-charging section, where it is converted to DC for charging. When the main supply fails, the inverter switches to battery power and provides AC output to the load.
Types of Inverters
Sine Wave Inverters:
These are the most common type and are suitable for everyday home appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, computers, and TVs.
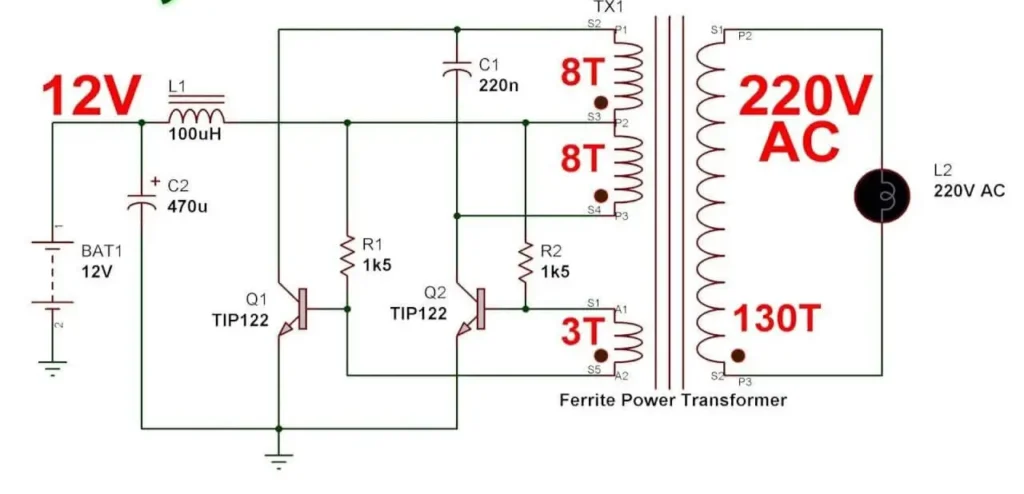
Modified Sine Wave Inverter
These are the inverts that are cheaper than the inverter, as mentioned above. They are used in low electrical devices like fans, bulbs, microwave ovens, etc. They convert 12-volt batteries and recharge them with solar panel generators.
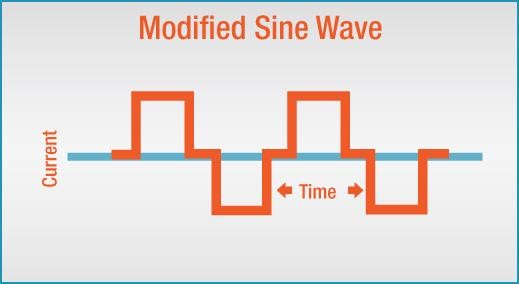
Solar Inverters
These are the inverters with more advanced features, and instead of using traditional energy, they use solar energy to convert Direct current to Alternating current.
Electrical Specifications of an Inverter
The inverter internally is made up of switches, a transformer, a battery, a MOSFET, and an amplifier. The DC which is stored in the battery is altered to the AC. The switches play an essential role in this process, where they are continuously turned ON and OFF. The MOSFET, a transformer, also consistently turns ON and OFF the DC voltage, making an opposite voltage, an alternating voltage.
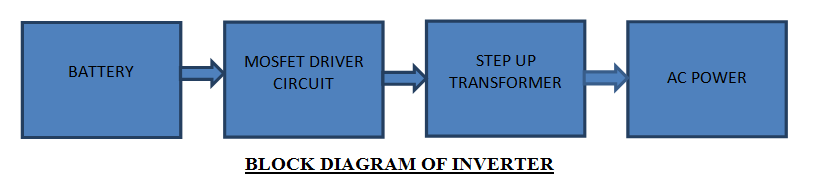
How to Make an Inverter Circuit Diagram?
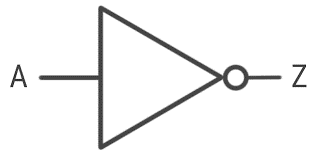
Before jumping into the inverter circuit diagram, it is necessary to know the logical symbol of the power inverter. In the electronics or logic design subject, the inverter is also known as the NOT gate, which does nothing but logical negation. Elaborating more, the inverter or NOT gate makes the high a low and the low a high.
The inverter is an important topic in the electronics and logic design world as the state machines, decoders, multiplexers, etc., use it for their working. In the same topic, if you have no inverter that is NOT gate, you can make it with the combination of NAND and NOR gate.
The logic symbol of the inverter is illustrated below.
Steps to Make an Inverter Circuit Diagram
To build a simple 100-watt inverter for a project, you’ll need a few basic components and a diagram-making tool.
Required Components
- 12V battery
- 0.1µF capacitor
- 0.01µF capacitor
- 390kΩ resistor (1)
- 1kΩ resistors (2)
- 220Ω resistors (2)
- 330Ω resistor (1)
- Switch (1)
- CD4047 IC (1)
- IRF540 MOSFETs (2)
How to Create the Diagram
Use any circuit-design software (e.g., EdrawMax) and open the electrical engineering section. Add the needed component symbols by dragging them onto the workspace or searching for them by name. Then place connector symbols and link all parts according to the inverter layout or your design requirements. This will give you a complete and accurate inverter circuit diagram.
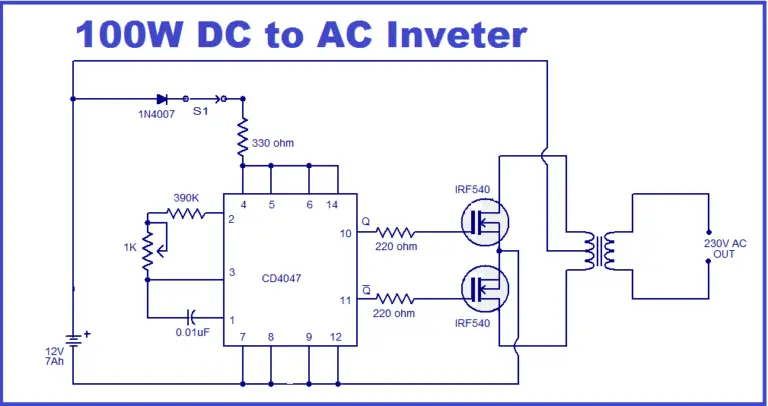
- From the software’s text feature, write all the component’s values and the short names.
- Now your project is ready to download. Use the software and download it.
The importance of using an Inverter
The inverter plays a vital role in our daily life. The equipment that uses inverter saves energy costs up to 50%. These types of equipment make less noise than the equipment without inverters. Plus, they are more stable while working.
The inverters can easily manage the changing temperatures of the devices. They can easily calculate the voltage, current and then work according to it.


