Ohm’s Law
This animation demonstrates Ohm’s Law, the fundamental relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in a DC circuit.
It shows how changing the supply voltage or resistance directly affects the current flowing through a resistor.
Ohm’s Law is the foundation of all electrical calculations in both basic and advanced circuits.
Key Components:
- Variable Power Supply: Provides adjustable DC voltage to the circuit.
- Resistor (100 Ω): Limits the flow of current and provides a fixed resistance value.
- Voltage Display: Shows the applied voltage across the resistor.
- Current Display (mA): Shows the current flowing through the resistor according to Ohm’s Law.
Working Principle:
Ohm’s Law states:
V = I * R
This means the current in a DC circuit depends on the voltage applied and the resistance present.
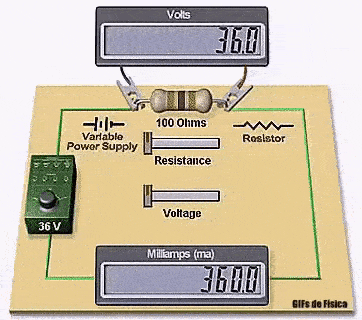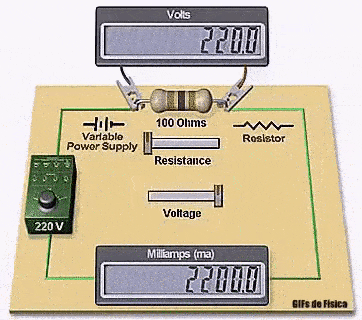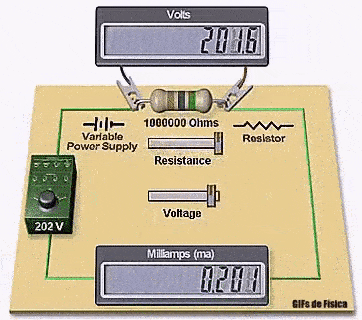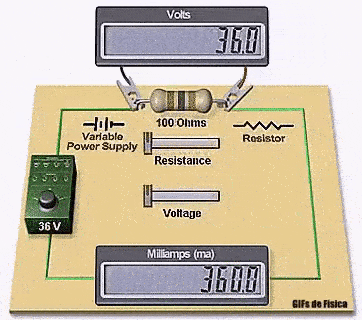
In the GIF:
- The supply voltage is 36 V
- The resistor value is 100 Ω
- The current shown is 360 mA
This matches Ohm’s Law:
I = V / R
I = 36 / 100
I = 0.36 A
I = 360 mA
The animation clearly shows how the voltage, resistance, and current displays adjust together to follow this exact relationship.
⚡ Tip:
If you increase voltage, current increases.
If you increase resistance, current decreases.
Always use the correct resistor to prevent overheating or excessive current flow.


